Artificial Intelligence Applications for Industry 4.0: A Literature-Based Study
Abstract
Artificial intelligence (AI) contributes to the recent developments in Industry 4.0. Industries are focusing on improving product consistency, productivity and reducing operating costs, and they want to achieve this with the collaborative partnership between robotics and people. In smart industries, hyperconnected manufacturing processes depend on different machines that interact using AI automation systems by capturing and interpreting all data types. Smart platforms of automation can play a decisive role in transforming modern production. AI provides appropriate information to take decision-making and alert people of possible malfunctions. Industries will use AI to process data transmitted from the Internet of things (IoT) devices and connected machines based on their desire to integrate them into their equipment. It provides companies with the ability to track their entire end-to-end activities and processes fully. This literature review-based paper aims to brief the vital role of AI in successfully implementing Industry 4.0. Accordingly, the research objectives are crafted to facilitate researchers, practitioners, students and industry professionals in this paper. First, it discusses the significant technological features and traits of AI, critical for Industry 4.0. Second, this paper identifies the significant advancements and various challenges enabling the implementation of AI for Industry 4.0. Finally, the paper identifies and discusses significant applications of AI for Industry 4.0. With an extensive review-based exploration, we see that the advantages of AI are widespread and the need for stakeholders in understanding the kind of automation platform they require in the new manufacturing order. Furthermore, this technology seeks correlations to avoid errors and eventually to anticipate them. Thus, AI technology is gradually accomplishing various goals of Industry 4.0.
1. Introduction
The applications of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies enhance the capabilities significantly in the manufacturing sector as it works across various business lines and levels, from staff planning to product design, maximizing performance, product quality and employee well-being. Advances in AI are central to various advancements, allowing robots to manage more computational tasks and make independent decisions based on environmental data in real time for Industry 4.0. It includes managing different criteria such as content types, manufacturing methods, budget limits and time constraints. The ideas and other essential tasks can be managed and evaluated using machine learning (ML), providing further insight into the latest designs. AI is used in factories to allow the predictive management of sensitive industrial machineries to predict asset failure in Industry 4.0. The administration is helped to timely rehabilitate the facilities to avoid expensive unplanned downtime (Yao et al., 2017; Lee et al., 2018; Bécue et al., 2021).
AI algorithms help businesses to predict shifts in the markets to maximize production supply chains. This offers management an enormous benefit from a reactionary to a competitor. AI algorithms estimate market demands by searching for position trends, socio-economic and macroeconomic variables, environmental patterns, status policy, customer behavior and more.
This development would allow manufacturers to reduce production downtime and optimize their manufacturing lines’ overall operating effectiveness. In addition, AI and computer training increase quality management and standardization by producing a predictive analysis of the equipment’s features and streamlining production lines ultimately. With AI implementation, industries can now take fast, data-driven decisions, simplify production processes, minimize operating costs and enhance customer service (Dal Mas et al., 2019; Haenlein et al., 2019; Gupta et al., 2021).
With an AI-compatible smart plant, manufacturing will work unprecedentedly, reduce costs and improve customer service. Industries can avoid downtimes by forecasting delays, control inventory by tracking stocks, anticipate the delivery speed and provide the highest quality goods. In order to monitor the production process and detect mistakes such as the microscopic crack in production facilities, computing vision may be used. AI may alert companies to production line problems that may lead to quality problems. The serious ones can be avoided in the early stages of the overall development level of Industry 4.0 (Javaid and Haleem, 2019; Ibrahim and Hassan, 2019; Sanchez et al., 2020).
Advanced AI algorithms in deep learning and artificial neural networks are used for repair prediction to formulate asset failure predictions. Quality requires AI algorithms to report evolving production defects to manufacture teams that can trigger product quality problems. This can analyze slight machine behavior abnormalities, changes in raw materials, etc. In order to ensure that a maximum algorithm produces values within the given interval, the product designer often establishes minimum and maximum limits. The results given are solutions that can be evaluated further with the help of ML to obtain insights into which architecture satisfies standards. AI algorithms are used for quality management to alert production units of possible production faults, leading to problems with product quality (Cheng et al., 2016; Koh et al., 2019; Bousdekis et al., 2020).
Manufacturing industries use this technology to produce a virtual representation that replicates factory, product or physical characteristics. By using cameras, sensors and other data collection techniques, this reflects real-time knowledge. Combining interactive and physical environments makes it possible to track plants, analyze data and solve issues proactively. The flaw detecting method in production lines becomes smarter in manufacturing. A computerized device can detect various surface defects such as scratches, cracks and leaks and others with deep neural network integrations. Data scientists teach visual inspection systems to identify defects according to their mission by applying image recognition, object identification and instance segmentation algorithms (Haleem et al., 2020; Massaro et al., 2020).
ML modeling will forecast energy demand in the future by handling historical data on consumed energy. The popular ML method is focused on sequential data measurements to forecast energy consumption. AI can permit systems to monitor themselves to reduce downtimes, maximize resource uses and anticipate failures (Mazurek and Małagocka, 2019; Chen et al., 2020). It can aid decision-makers in testing environments, increase the efficiency of assets and prevent system failures. It will help organizations appreciate their products by visualizing the performance of their products in their factory environment and in real time by the workforce. The information obtained from the simulated reality will be used to turn the product concept into potential goods in the real universe (Bortolini et al., 2017; Milward et al., 2019).
2. Research Method
This is review-based research reporting from different research papers, blogs and other research platforms by searching the keyword as “artificial intelligence”, “Industry 4.0”. This paper addresses the following research objectives:
| • | To brief about AI for Industry 4.0 and discuss technological features and traits of AI for Industry 4.0; | ||||
| • | To study significant advancements of AI and discuss various challenges in implementing the AI concept for Industry 4.0; | ||||
| • | To study diversified sets/subsets of AI for Industry 4.0; | ||||
| • | To identify significant applications of AI for Industry 4.0. | ||||
3. Artificial Intelligence in Industry 4.0
In Industry 4.0, AI integrates numerous technologies that enable software and machines to sense, comprehend, act and learn human operations. The industrial production system can be more efficient using this technology. The manufacturing sector is constantly growing because this technology advances with Industry 4.0. AI is one of the developing technologies used to increase efficiency, product quality and reduce operational costs. The smart factory comprised of hyperconnected production processes comprises multiple machines that all communicate with one another. Manufacturers undergo a digital transformation that manages and uses their data sets by leveraging AI and ML for better quality control, standardization and maintenance. The benefits of AI in manufacturing processes are numerous in day-to-day services in Industry 4.0 (Ibrahim and Hassan, 2019; Chi-Hsien and Nagasawa, 2019; Zhang and Lu, 2021). It is utilized to speed up our job by producing more accurate results with less human effort. It makes use of digital technology, which makes Industry 4.0 smarter and more productive. AI advancements give rise to computing systems that can see, hear, learn and open innovative platforms to improve skills.
3.1. Artificial intelligence
AI refers to human-like intelligence demonstrated by machines like natural intelligence, which helps solve problems of varied nature. AI has a significant effect on the production areas that can perform various tasks just like human intelligence. The use of AI technology in the production supply chain will predict product demand’s time, geographical and socio-economic dynamics in various algorithms, accounting for macroeconomic cycles and weather patterns (Tung, 2019; Xu, 2021). The predictive management of equipment with sensors to track working conditions and tooling efficiency is also highly advantageous to AI. This technology can address many of the industry’s internal problems, from skill shortages to decision-making complexities, deployment difficulties and overflowing knowledge. Using AI in production plants allows companies to transform their procedures entirely. The use of AI and robotics in industrial production is mainly observed since mass production is revolutionized. Robots will carry out recurring tasks, design the development model, increase competence, develop strategies for building automation, eradicate human error and provide superior quality assurance (Nascimento and Bellini, 2018; Merayo et al., 2019; Ammar et al., 2021).
AI gives companies a sophisticated level of analysis that they can use to analyze their individual components’ results. The AI database analysis can increase a facility’s total performance and improve the output quality. It allows robots or other equipment intelligent enough to sense abnormalities and track parameters. It detects, summarizes and analyses the massive data flow, then passes it to other computers to a cloud-based network. It helps to manage a large-scale flood and enables an internet of things (IoT)-scale ecosystem to be leveled. AI helps program creators and broadcasters to detect which shows they can suggest to specific consumers based on their behavior by entering the entertainment industry. ML algorithms are used for user behavior, and such algorithms become smarter with time to determine user requirements also (Badri et al., 2018; Cioffi et al., 2020; Radanliev et al., 2021a).
3.2. Industry 4.0
The word Industry 4.0 applies to the implementation of advance information and manufacturing technologies in industries. This is the term often used for the digital revolution in the industry. It is a global word that refers to AI Cyber, IoT, cloud, ML, etc. These can be intelligently interpreted and developed in the manufacturing processes. It can quickly assess the data gathered during the manufacturing process. New processes are obtained via this assessment and can constantly adjust output changes. Various processes are also not only better linked in this industrial revolution but also streamlined. Industry 4.0 is the pavement for digitization in the industrial industry, which changes how we communicate with and revolutionizes AI and ML applications (Hofmann et al., 2019; Cioffi et al., 2020).
One of the key objectives of Industry 4.0 is to operate the computers in a decentralized and autonomous manner in cases of exceptions, interferences or overlapping objectives requiring external feedback. The application of AI has led to positive changes in their intelligent factories that reduce maintenance costs. Furthermore, advances in industrial cybersecurity technologies often allow corporate network surveillance to tackle hacker attacks in good time. Industry 4.0 provides the latest development in industrial technology automation and data sharing. AI can be easily determining their future manufacturing with the effective storage of data. The more the machines data sets are fed, the more patterns are evolved, learned and decided with the interest of the production company. This automation helps correctly forecast errors, predict working loads, track problems and expect them (Haleem and Javaid, 2019; Dudukalov et al., 2021).
3.3. Need of artificial intelligence for industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 needs to prepare for networked factories that are highly embedded in the supply chain, design team, production line and quality control into a smart engine that provides practical insights with the help of AI. To exploit Industry 4.0’s many opportunities, manufacturers need to develop a system that considers the whole production process as it needs cooperation across the whole supply chain cycle. Today, the main fields of AI, ML and IoT adoption are asset control, supply chain management and resource management. Combining these new tools, asset tracking precision, the visibility of the supply chain and stock utilization can be improved. Predictive maintenance can be improved using ML strategies like algorithms, processes powered by machine intelligence and quality optimization (Shi et al., 1995; Kunst et al., 2019; Javaid and Haleem, 2020). Effective time monitoring of operating loads at the factory floor contributing to production planning efficiency can be quickly undertaken using AI. By combining ML with overall equipment effectiveness, producers can increase production, preventive maintenance and asset workloads.
4. Technological Features and Traits of Artificial Intelligence for Industry 4.0
Figure 1 reflects the various technological enablers of AI, which fulfills the requirements while implementing this philosophy in Industry 4.0 culture. There are four different traits: operations technology, data technology, analytics technology and platform technology (Chen and Li, 2019; van Geest et al., 2021). These enablers support the AI practice to make the Industry 4.0 sphere more accurate, precise, quick, optimized and secure to make Industry 4.0 more effective and realistic.
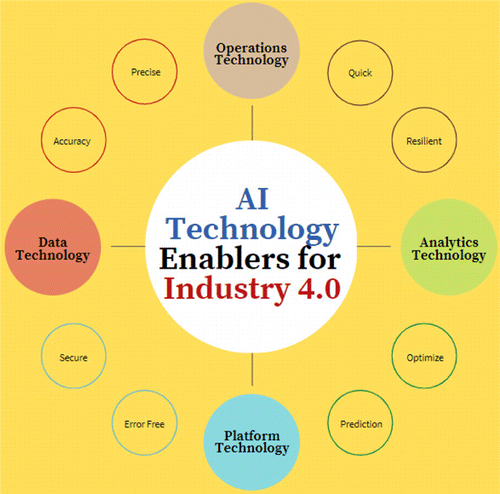
Fig. 1. Various tools and traits of AI for Industry 4.0.
AI has a binding effect in manufacturing on the intelligent maintenance of the development system. This provides predictive solutions to prevent sudden harm to equipment. AI-enabled solutions for manufacturers will prevent equipment failure before it gets affected. The fact that production data is fantastic for AI drives this popularity. The production is full of empirical data that is easier to interpret for robots. Hundreds of variables affect the output process while they are challenging to analyze in human environments. The effect of individual variables in complex situations can be predicted effectively by AI models. Machines can operate under human capacity in other sectors that include language or feelings. AI enhances the quality management of industrial systems. AI-based systems spot component flaws on the manufacturing line (Chen and Xu, 2001; Tang et al., 2001; Romeo et al., 2020; Bogoviz, 2020).
There is unbelievable use of AI in Industry 4.0. Industrial AI robotic cooperation allows producers to supply generative materials more quickly. AI is transforming how designers design goods in the industrial sector. The AI production solutions have guidance into the suitable models. A digital twin is used to track and assess the manufacturing process and determine whether quality problems can arise or whether the product output is less than expected. Digital twins allow producers to have a clear picture of the used products and allow the refilling process to be automated. Manufacturers use AI technologies for the analysis of sensor data to detect possible downtimes. Manufacturers assist AI systems in predicting whether or when functions will malfunction so that servicing and repair can be planned for the failure (Skobelev and Borovik, 2017; Sharma et al., 2021).
The automotive sector continues to embrace AI services to modernize its activities. It has special applications that can turn a modern production company entirely. AI can predict the competition and reliably evaluate the potential benefit of goods when they are in demand. AI software programming can allow producers to reduce electricity prices and adverse market fluctuations by enhancing demand forecasting while operating. The integration of AI algorithms in procurement, industrial sourcing and cost control. It is already underway in business and consumer goods, technical facilities and aircraft applications for various customers to enhance product requirement projections in their workstream. This technology derives its strength from the data collected from instruments or sensors installed in manufacturing machinery (Preuveneers and Ilie-Zudor, 2017; Jimeno-Morenilla et al., 2021).
Generative programming uses the algorithms of ML to represent the approach of an engineer to design. Designers enter design parameters into the design program, and the software produces all possible results that these parameters can provide. This technology easily allows designers to create thousands of design alternatives for a component. Businesses need to adjust to the unstable raw material price to continue to compete in the market. The preservation of the optimal standard of consistency in a process or good is quality assurance. It enhances the assembly line’s capability to operate based on parameters and algorithms that provide the best final goods. AI systems can distinguish deviations from the standard performance with machine viewing technology because most defects are noticeable. If the output of an end product is less than intended, AI systems will cause a warning for users to respond (Xu, 1999; Feng and Xu, 1999; Paolanti et al., 2018; Kebisek et al., 2020).
This technology stepped up attempts to adopt digital transformation to meet changing customer needs. In Industry 4.0, analytics and the IoT will be instrumental in defining trends, behaviors and providing in-house evidence on the manufacturer. Manufacturers expect to optimize intelligent resources based on the gathered data from different intelligent workflows and processes of the plant. The ultimate aim in the automotive sector is a prompt and reliable distribution to a customer. However, it is impossible to develop a reliable distribution chain with several facilities in various areas. Using a process mining tool, manufacturers can compare each area’s output by each step, including time, cost and the person taking the step. These findings help streamline operations and determine the location of bottlenecks so that companies can respond (Samarasinghe and Medis, 2020; Tiwari and Khan, 2020; Borowski, 2021).
Artificial neural networks are ideal for the variable and continuously evolving production processes to process several parameters across many layers. It needs adequate training to demonstrate high precision in producing predictions of the mechanical properties of processed goods, which reduces the costs of raw materials. The trend of business, propelled by the modern mode of contact between human beings and the computer, has changed AI. Smart plants consume automated facilities and have digitally-enabled devices that allow machinery to communicate via IoT configuration between them and the factory systems. Industries are increasingly demanding these skills to ensure the productivity of the manufacturing plants (Tarassov, 2018; Ng, 2020).
5. Significant Advancements in Industry 4.0 Through Artificial Intelligence
The successful launch of autonomous vehicles and robots shows the integration of AI and ML. The use of sensors in combination with ML helps the output of each development phase be continually evaluated. The adapting of supply to demand is one of the common problems in the industry. The integration of ML helps to fulfill energy requirements optimally. AI technologies are also used to improve user service. For example, many chatbots on e-commerce sites came with AI-driven and configured so that several typical consumer questions can be answered instantaneously. The agricultural sector saw an increase in the use of sophisticated tractors and smart plucking machines. Fraud detection in the financial sector is another significant application of AI (Chun et al., 2018; Haleem et al., 2019; Leng et al., 2021).
Nowadays, robots are an integral part of the manufacturing company’s machinery. These robots have now made intelligent decisions and work together to maximize productivity in production facilities in conjunction with AI technology. AI can be quickly operating self-driving or semiautonomous cars. It becomes part of network-linked and run-on roads depending on various circumstances. The AI systems of vehicles can forecast the driver’s actions, classify the passengers, assess conditions on the way and traffic congestions to track vehicle driving. Self-driving cars are sure to be the next major thing in the automotive business. While AI self-driving is still in the research and test stage in many countries, it can replace manual driving and move safer on roads. The use of AI in the immobilizing sector provides agents, brokers and customers all with new resources. AI-powered companies help dealers and agents to find the right solution for those looking for their assets to purchase and sell (Kempegowda and Chaczko, 2018; Ruiz-Sarmiento et al., 2020; Kliestik et al., 2020).
Industrial firms invest in automated AI vehicles to automate logistic processes to help control the delivery centers. Self-driving cars thus eliminate dependence on human drivers. The demand for products can also be effectively predicted by AI systems using predictive analytics. AI manufacturing applications gather data from different sources. Later on, it can forecast product demand correctly based on evidence. The AI app can handle order records and uninstall/install new stocks. It is one of the finest technologies for production management, market management and inventory management. Through analyzing historical product–price data, algorithms for ML will predict the price of a product. It can use neural networks and in-depth modeling to recognize images and supervise predictive model learning (Dhanabalan and Sathish, 2018; Helmold, 2019).
AI helps the robot to accurately capture tiny air bubbles and assess the position of the gas leakage. It quickly locates trouble areas and production lines and significantly reduces labor cost and detection errors, along with data extracted from the entire production chain. Sensors are built into each hardware piece in Industry 4.0 environment to communicate from machine to machine. Moreover, ML provided by data-physical systems and cloud computing makes linking humans, machinery and resources seamless. As a result, all aspects, including vehicles, manufacturing lines, factories and facilities, in the production process can be connected closely.
6. Various Challenges in Implementing Artificial Intelligence for Industry 4.0
Factors related to data quality, machine-to-machine variations, cybersecurity and operational regimes are major identified barriers to effectively realizing the AI practice for enhancements in Industry 4.0. For example, Fig. 2 shows various associated challenges in implementing AI methodologies in Industry 4.0 sphere. It ultimately correlated with the perfection, reliability, error freeness and completeness of the data; variableness, controlling, capability and automation of machine-related variations; diagnosis, system analysis and assurance factors are associated with operational schemes (Tang and Veelenturf, 2019; Ribeiro et al., 2021).
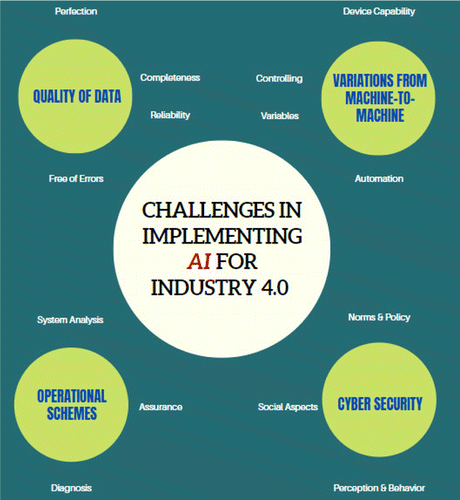
Fig. 2. Associated challenges in realizing AI for industry 4.0.
AI is being used to classify and accurately diagnose and handle a wide variety of health care facilities, including data mining to identify trends, medical imaging, pharmacy management, pharmaceutical detection and robotic procedure. Retail companies are constantly looking to find trends for customer behavior as a competition space and thereby match their approach with their competitor’s intelligence. AI tools will monitor client behavior so that trends can be identified and potential results are predicted. Companies can better respond to their demands by observing the actions of current consumers. AI is the best tool for every company that changes the game. It is becoming more available to businesses as the platform matures and costs decrease. It can be helpful in production to make things safer and cheaper. The industrial sector has already looked forward and effectively adopted emerging technology (Frank et al., 2019; Benotsmane et al., 2019; Singer and Cohen, 2021).
AI can easily carry out manufacturing, quality management, shorter design time and waste reduction, improved reuse of production and predictive maintenance. Predictive maintenance enables businesses to determine whether machinery needs high precision maintenance rather than preventive maintenance. Predictive maintenance avoids the use of ML unplanned downtime. In the production equipment, technologies like sensors and advanced analytics allow for predictive maintenance by addressing system problems and managing warnings. AI experts concentrated for some time on the identification of patterns and computer pedagogy. ML is central to the identification of images, faces and words. Audio–vision processing, digital translation or transcription and driver-free vehicles are the other noteworthy applications (Uslu and Fırat, 2019; Gomes et al., 2020).
AI may ingest a mixture of the sensor, computer and human data, refine operations or achieve production lights. The intelligent production plant consists of hyperconnections comprised of interconnected computers, which use automation platforms for AIs to capture and analyze all types of information, including images and standardized tests. Manufacturing deploys AI to incorporate automation frameworks for managing various tasks. It also encourages workers to simultaneously use the same computer to execute other tasks, thereby reducing human contact. Using AI, a manufacturer may warn workers of problems with a project in a short space of time. No longer any digital revolution is overlooked, and AI programming has a major and vital role in the industry’s future. Manufacturers will adopt and implement manufacturing-revolutionizing AI technologies (Terziyan et al., 2018; Rizvi et al., 2021).
The standard manufacturers can now start to adopt ML models for cost savings aggressively. While most manufacturing processes have been researched for decades, recent development has opened up a new frontier for further optimization in AI, particularly ML. It allows one to create a paradigm that takes data from various sources into account. AI means that fewer human resources are harmful and minimize the number of mistakes in the production plant. The number of injuries at the workplace will decline as robots overtake human beings and conduct regular and dangerous tasks. When AI takes over the production facility and automates repetitive and ordinary human jobs, employees concentrate on creative and complicated activities. People should concentrate on pushing creativity and driving business to advanced stages using AI (Yan et al., 2017; Pereira et al., 2020).
In recent years, AI and factory automation have progressed significantly. The development of deep learning algorithms and developments in sensor technology have led to a new generation of developing computer resources. AI helps machines collect and remove data, recognize models, learn and adapt through master intelligence and recognize learning and language. In addition, AI is excellent at interpreting and decoding natural language. This would make communication with the app easier for employees and managers. Inventories costs can be reduced using AI, which creates robust advancement for the manufacturing industry. The productive industry needs to be equipped for integrated manufacturing plants, which are very structured in the product line and quality management (Lafferty, 2019; Lăzăroiu et al., 2021). For example, a factory worker should procure raw material reserves from the shelf and immediately establish the inventory transaction using a monitoring camera.
7. Diversified Sets/Subsets of AI for Industry 4.0
Figure 3 exemplifies distinct sets and subsets related to practicing AI methodologies for improving and enhancing the Industry 4.0 environment. In this perspective, ML, cognitive computing, the IoT, factory-based industrial automation, robotics and big data-related aspects are needed to be taken care of while realizing Industry 4.0 through the support of AI (Wan et al., 2018; Pires et al., 2019).
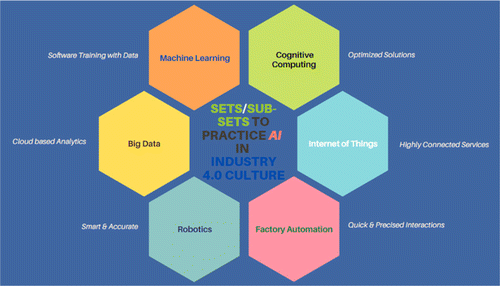
Fig. 3. Different sets/subsets of AI for industry 4.0.
AI enhances Industry 4.0 to improve their demand forecasts and ensure that supply increases and decreases as needed. In the production industry, AI focuses primarily on reducing downtime and ensuring the continued effectiveness of production lines. When replacement parts must be ordered, AI may be used to forecast. This skill eliminates plant machinery downtimes and prevents costly components from being stocked. It can be done by adding vast quantities of data and modeling that indicates a possible component malfunction. ML models continuously interpret data unique to the company and production, making it more precise and preventing errors and anomalies. The whole supply chain can be controlled by AI and foresee any changes in demand that can influence production processes (Bai et al., 2020; Popkova and Sergi, 2020; Lee and Lim, 2021).
Digital twin AI technology gives engineers the capability to view and test components, manufacturing lines more remotely. With today’s cloud-enabled power rental capability, small and large enterprises may use AI technologies to identify bottlenecks, weaknesses and errors and improve functionality that speeds up their time on the market. Engineers can see how everything interacts with many data and map connections between materials, devices and systems. AI can autonomously upgrade the specification based on real-world information. This technology adoption will contribute to mass personalization and significantly enhance versatility. Manufacturing may have highly ineffective procedures, which are usually refined and modified continuously (Angelopoulos et al., 2020; Hansen and Bøgh, 2021).
AI can produce data that allow making sound, factual and data-oriented business decisions. This also helps to remove individual prejudices from the calculation, and in many ways, to provide a more detailed overview. Data from various sources can be collected through an AI platform and ML technologies. AI allows producers to remain competitive, cut prices, optimize resources and provide their workers with a better workplace and customer experience. Large production companies started using AI to make purchases of materials and allocation decisions. AI would also improve manufacturers’ standards for launch dates and capacity-based volumes along with unplanned downtime. This technology will support businesses to determine what to do with their replacement potential, such as early production of seasonal goods sold at low cost to retail stores in the year (Candanedo et al., 2018; Azizi, 2020; Mhlanga, 2020).
In most businesses using standard data, early progress will generally come when supervised AI demands good data and proper preparation. In other words, as solutions start to appear, businesses follow AI. Industries of easily accessible high-quality data then provide AI applications ready for use as quickly as possible. Better vision software will facilitate quality on a mass scale with fewer workers. It is likely to affect task analyzing data and propose market optimization activities, from architecture to process and service. The architecture of the product is often severely interfered by AI. This provides generative design methods that identify the problem, compute the whole problem area and amplify cognitive skills (Pilati and Regattieri, 2018; Lu, 2019).
AI can also improve design products by proposing solutions by generative design tools based on the comprehensive overview provided by engineers and designers. In order to devise estimates of market demands, AI algorithms can research consumption, weather, socio-economic and macroeconomic and geographical trends. The data will help manufacturers anticipate shifts in the industry and optimize their energy usage, stock levels, raw material procurement and staffing to adapt more effectively to market changes. The next step in industrial technology is to link robots, computers and machinery to the IoT and improve it with ML algorithms. AI is one of the latest tools that manufacturers use to increase product consistency, effectiveness and reduce running costs (Özdemir and Hekim, 2018; Zheng et al., 2018; Sajid et al., 2021).
The transition from conventional automation focused on autonomous industrial robots to networked. Cyberphysical structures have revolutionized the functioning of manufacturing plants and introduced new competition requirements of Industry 4.0. The AI-driven production systems can tailor the production of components to the order. Sensors monitor components by ordering them to shorten lead times according to demand and algorithms. Manufacturing lines become information systems that feed decision-making in matters that are fundamental to the product line. It gives a concise view of what needs to be targeted next by drawing action items for the Industry 4.0 transformation plan. In order to improve productivity and add to the requisite multiadaptivity, the main aspects of Industry 4.0 reveal an AI for the IoT (Radanliev et al., 2020; Chetthamrongchai and Jermsittiparsert, 2020; Mhlanga, 2021).
8. Artificial Intelligence Applications for Industry 4.0
AI strengthens companies’ analytical capacity to make accurate predictions and use their resources more effectively and minimize stock costs. There are many potentials to apply AI and ML in production. For a wide range of applications like production process modeling and predictive quality analytics, artificial neural networks have proven to be an incredibly efficient learning platform. AI is adopted for defect identification and decreasing waste to raise revenue projections. It also gives market managers an idea about updating business models as per the changing manufacturing sector. This technology is used for the real-time detection of defects. If several products show the same defect, the mistake can be corrected in real time (Salkin et al., 2018; Hou et al., 2020).
This helps businesses to schedule manufacturing lines well in advance, forecast demand and order inventory. As a result, projections in the supply chain can fluctuate depending on a range of variables that can be very difficult for man. This will save enormous time and resources because this sensitive technology limits waste from defects without human interference and further ensures that better products of extreme performance are manufactured. Instead of depending on people for time-intensive in-process testing and quality management, AI will help accelerate procedures and improve precision. The production methods, efficiency, protection, facility maintenance, logistics and manufacturing are manual, labor-intensive activities and processes (Bibby and Dehe, 2018; Peres et al., 2020). Table 1 shows significant applications of AI for implementing Industry 4.0.
| S. no | Applications | Description with references |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Helps to perform a routine task | AI-enabled industrial robotics are used for automatic processing and performing routine tasks. This can avoid and minimize human bugs to a marginal pace using this technology. Assembly, welding, paint, stock testing, pick-up and putting, die molding, boiling, glass production and grinding are included in the applications. An industrial robot can track its accuracy and efficiency and prepare itself to improve with AI. Some production robots are equipped with this technology, which helps the robot in complex and random environments to achieve precision mobility (García, 2019; Sima et al., 2020; Javaid et al., 2020; Zheng et al., 2021). |
| 2 | Production planning and demand forecasting | ML systems encourage resource planning, and they are good at handling production planning and demand forecasting. AI-driven demand prediction systems produce more precise outcomes than conventional demand prediction. Industries can handle inventory volumes better and thus reduce the likelihood of cash-in-stock and off-stock situations. Technology driven by AI will help companies refine processes for achieving sustainable levels of output. Manufacturers can prefer process mining software powered by AI to detect and remove bottlenecks from organizational processing (Singh et al., 2019; Banjanović-Mehmedović and F Mehmedović, 2020; Ashima et al., 2021). |
| 3 | Increase awareness of the product | AI helps producers to increase their product awareness and encourage companies to experiment with potential measures to improve asset efficiency. Until manufacturing its physical equivalent, manufacturers may use digital twins. This application allows companies to gather data from the virtual twin and develop the original data-driven product. Because of the change in market appetite for personalization, producers can employ digital twin devices to design different product permutations. This encourages consumers to buy the product based on output measurements instead of its architecture (Li et al., 2017; Popkova, 2019; Felstead, 2019; Hughes et al., 2020). |
| 4 | Better monitoring and safety | AI provides better monitoring and safety and has become one of the most common causes of usage. This technology can be used for staff identification, thermal scanning or monitoring employee contacts for touch tracking and sanitation. AI had contributed to long-term protection solutions before they occurred or accelerated detection of the root cause after the occurrence. These solutions can contribute to happier staff, safer jobs and ongoing employment. AI reduces downtime and guarantees high-quality end goods in the production process. In addition, engineering firms use AI-based analytical solutions to enhance work performance in their data structures (Zhou et al., 2015; Diez-Olivan et al., 2019; You and Feng, 2020; Ahmed et al., 2021). |
| 5 | Appropriate information | In a production system, information for several minutes does not appear or go unnoticed by the human eye. Advanced technology such as ML and AI helps identify microscopic deficiencies in circuit boards well beyond human vision. Therefore, these technologies can provide appropriate information in Industry 4.0. Furthermore, collaborative robots are becoming increasingly common in manufacturing firms. Robots can interact with human associates and be guided by humans, including new commands that are not expected in the original programming of the robot. Therefore, improved computer senses would result in longer-term safety (Petrasch and Hentschke, 2016; Da Costa et al., 2019; Oztemel and Gursev, 2020; Haleem et al., 2021). |
| 6 | Designing and manufacturing | In the manufacture of goods with generative architecture, AI plays an important part. It is an iterative design process that includes feeding into the AI algorithms of comprehensive design details. This knowledge can cover many design criteria, including processing methods, nature of the product, time limits and budget constraints. The algorithm will examine any possible solution permutation by taking all these parameters into account and have the most appropriate output solutions (Cotet et al., 2020; Masood and Sonntag, 2020; Duft and Durana, 2020; Khayyam et al., 2020; Radanliev et al., 2021b). |
| 7 | Detection of defects | ML and AI technologies can be beneficial here since cameras, lasers and scanning instruments can be linked to an AI program. It analyses objects as they travel down the production line. This technology is used for the real-time detection of defects. The several products show the same defect and can be corrected in real time. It will save enormous time and resources because this sensitive technology limits waste from defects without human interference. AI technology can produce valuable information that enables entrepreneurs to build innovative and robust business models. AI is beneficial at detecting patterns and phenomena where the ordinary human cannot see excessively (Bahrin et al., 2016; Olsen and Tomlin, 2020; Kushwaha et al., 2020; Stentoft et al., 2020). |
| 8 | Enhance product efficiency | Automatic learning greatly enhances production efficiency by integrating predictive algorithms for maintenance into manufacturing operations. AI can quickly replace visual checks with highly precise and powerful robots. The challenge of AI usage in Industry 4.0 allows manufacturers to work with experts to find adequate and customized solutions. For the implementation of AI, the industries become more efficient. While the transition in Industry 4.0 is still in its early stages, AI has already brought us major benefits. This technology has intended to change the way for producing goods and process materials forever from the concept and manufacturing floors (Massaro et al., 2018; Hayhoe et al., 2019; Chao et al., 2020; Teoh et al., 2021). |
| 9 | Quality assurance | AI would have a different effect on production. For quality assurance, products are used to improve computer vision for in-time detection of product defects as manufacturers recognize the importance of AI in the reliable, timely detection and maintenance of the manufacturing line. This technology can minimize downtime and enhance product development, and continuous service is gaining momentum. In addition, AI algorithms will warn manufacturing teams to emerge failures, such as subtle anomalies in equipment and other problems, triggering product quality problems (Lee et al., 2019; Bourke, 2019; Haleem and Javaid, 2020; Riley et al., 2021). |
| 10 | Optimize processes | AI technology optimizes processes and promotes high efficiency. The future plant is modular, clean and optimally uses capital to produce everything from individual goods to mass. In terms of Industry 4.0, such versatility needs to be of high maturity; human beings work together with robotics in mixed teams and are assisted by intelligent support systems in their tasks using this technology. The use of AI in Industry 4.0 offers both actual manufacturing facility possibilities and challenges (Hao et al., 2019; Davidson, 2020; Fatima et al., 2021). |
| 11 | Supply chain monitoring | Machine education, natural language modeling, machine vision, robotics and language recognition make the management of supply chains more intelligent. This technology provides many supply chain monitoring applications. The demand for products can also be effectively predicted by AI systems using predictive analytics. AI production tools gather data from different sources and can precisely predict product demand based on them. In addition, the AI apps can handle order records and uninstall/install new stocks (Abubakar and Adeshola, 2019; Tuffnell et al., 2019; Kumar and Gupta, 2020; Bag et al., 2021). |
| 12 | Production management | AI is one of the most important technologies used for production management, market management and inventory management. Machines can be more powerful than people. This is much quicker in the performance of tasks than people. AI-powered robots execute repeated tasks without being scheduled. AI enhance production, customer support sales and quality and market efficiency through smart management. The AI production system can deliver optimization of the processes, low operating costs, high quality, rapid decision-making and customer experience improvement (Ansari et al., 2018; Sanchez, 2019; Gray-Hawkins et al., 2019; Canito et al., 2020; Ivanov et al., 2020). |
AI allows manufacturing firms to deal with unforeseen downtimes, low yields and low productivity by quick feedback loops. In supply chain management, the use of AI is growing exponentially. This technology gains traction during activities of distribution chain management. The smarter functions in supply-line management include ML and natural language processing, computer vision, robotics and speech recognition. Warehouse logistics and processes can be optimized using AI software and applications. Tools and software with AI capability can also effectively control and monitor fleet activities (Carvajal Soto et al., 2019; Ludbrook et al., 2019; Villalba-Diez et al., 2019; Azeem et al., 2021; Massaro et al., 2021).
AI algorithms can easily report evolving production defects to manufacture teams that can trigger product quality problems. A high degree of consistency can be sustained by addressing these problems early. It also allows suppliers to gather information on their commodity use and success in the market. The AI algorithms can make the anticipation of demand trends in order to improve supply chains for manufacturing. AI-powered inspection tools have automatic procedures for fault detection. The smart equipment defect detecting tools in production track the equipment’s efficiency and condition (Avishay et al., 2019; O’Donovan et al., 2019; Tao et al., 2019; Neumann et al., 2021).
9. Discussion on the Findings
AI is introduced in Industry 4.0 for the massive transition of producer firms and will provide new business models and lead to changes in productivity. Predictive repair cost control leads to less maintenance, decreasing labor costs, lower inventory and wasteful materials. Management of the supply chain through efficient stock management and a well-controlled and syncing output flow can be quickly undertaken using this technology. A mixture of refined machinery and adaptive software is visualized as the future of the industry. The simplicity and scalability ensure great data analysis and cloud computing infrastructure. Through this technology, companies will optimize manufacturing processes.
In manufacturing processes, AI is utilized by original equipment makers who operate efficiently in smart factories and introduce Industry 4.0. This technology is used for better quality management, standardization and maintenance by predictive analysis of machinery functions and progressive rationalization of factory lines. Many businesses now want to incorporate AI in their manufacturing systems for better strategy and automation platforms. This makes it easy to adjust to demand and to move from the raw materials, joining the production chain to the finished product. Via knowledge networks, consumers are linked to the market and demand premium goods and interactions. Digital designs and smart development manufacturing companies can produce personalized goods without any productivity loss.
The use of AI in Industry 4.0 is a development that radically changes the market in the years ahead. AI is one of the best examples of emerging technology in manufacturing. The companies are helped to include high-quality goods by developing tools that use AI capabilities. In addition, AI is the best and modern technology that combines sensor device processes, machines and data for improving the overall operation. Data is collected via the sensors, transmitted via the internet to the cloud server and analyzed via ML and AI algorithms. It is then returned to an automated robot or a service terminal to complete a complete workflow. As a result, industries create greater user understanding, production, product quality control, delivery logistics and consumer input.
In today’s time, digital data must become compatible and refinable as a basis for new business models and monetization for the intensive use of AI and ML frameworks. In order to take suitable decisions, businesses need to be fully aware of their digitalization degree and Industry 4.0 willingness. Several indices have been developed for this purpose in the Industry 4.0 maturity evaluation of performance. Better quality control and feasible perspectives improved product quality continuously. Improved coordination with human machines improved safety and performance. AI enables risk analysis and businesses to identify breakdowns. The computers can be monitored in real time, downtimes prevented and total productivity increased.
In all industries, AI has led to transformative developments. It is implemented in every field, including hospitals, life sciences, immobilization, education, manufacture, etc. The AI revolution will turn vast volumes of data into practical observations and forecasts that offer an incentive for fields powered by data such as biology, robots, connected and smart systems, etc. As Industry 4.0 demands a relatively precise and comprehensive data flow, the different modules used in the manufacturing phase can be refined. As a result, each part of the manufacturing line is increasingly scalable and detailed, enabling individual production to properly embody and anticipate customers’ desires, thereby producing a virtuous circle of production–sales input.
AI is meant to transform the way we produce goods and process materials from the design and manufacturing floor to the supply and administration chain. Innovations have already been available to the automotive sector. Automation can enable production to achieve a high degree of precision and efficiency beyond human capacity. It can function in otherwise risky, tedious and challenging situations for human beings since large businesses rely on sizeable industrial manufacturing to achieve their competitive edge in our current stage of growth. The capacity of computers to mimic human intellectual skills is AI. They are equipped with electrical control circuits and electronic chips. These are the parts of AI that provide software mechanisms and maintain them.
The system is also supposed to deal with sensory functions. The device is very convenient for AI researchers to link up on the server. ML frees corporate knowledge and the management of decisions in a greater domain. There were hundreds of variables that influence the development process, although these are very difficult to interpret for people. ML models can easily predict the effect of individual variables in dynamic scenarios. Machines also operate under human capacity in other sectors that include language or feelings. For example, the maintenance of machinery and equipment production lines is higher in the industrial industry, which significantly influences any production process that connects with assets.
Computer education and predictive analytics have turned management of the supply chain into a smooth operation. For sorting and packing goods, warehouses are using AI-enhanced robots. In addition, AI algorithms are being increasingly used to identify the fastest shipping route and facilitate the distribution of goods to customers at various places. The availability of extensive data on how the goods are evaluated and how they work describes the various fields that need to be tested for AI software and machines. Predictive system management enables manufacturers to prevent overhead disruption to equipment. It can determine whether machinery requires repair services through AI-powered predictive analytical solutions.
10. Future of Artificial Intelligence in Industry 4.0
AI will provide valuable information that enables corporate executives to develop innovative and robust business models. This system will become highly useful at detecting patterns and phenomena where the ordinary human cannot see excessively. AI will produce data to allow to make sound, factual and data-oriented business decisions. It will also help to remove individual prejudices from the calculation, and in many ways, provide a more detailed overview. AI and ML tools can gather data from several different sources and find growth, extension and even new market opportunities, and new products and services will be developed. Other innovations such as blockchain and edge computing have become more popular, and their fusion with IoT also provides new applications. Soon, AI will boom with new advantages that will help to create a wired, intelligent and smart society. For example, manufacturing may have highly ineffective procedures, which are usually refined and modified continuously. Robotics as a service would have the capacity to recreate specific human functions in the future, such as speech and image recognition, with the help of AI. It can track, analyze production quotas and can contribute to predictive maintenance models.
11. Conclusion
Industry 4.0, with the help of AI, completely automates the control of the different stages of the production processes. Based on the product specifications, any stage of the manufacturing procedure will be refined in real time. It can integrate the complete development chain, and the job load involved in data processes can be extended to many divisions. The data collection systems and data feedback systems can be incorporated into manufacturing processes through AI. This technology can share assembly lines with production processes to increase efficiency. Advanced AI algorithms are used for repair prediction and to formulate asset failure predictions. The integration of AI with Industry 4.0 provides various industrial developments. AI can better manage the related output processes. This technology can create meaningful perspectives that contribute to creativity in manufacturing. The physical representation of the production environment is fully visualized with data collection instruments such as sensors and cameras. The data generated by intelligent components are gathered, saved and processed using a cloud link. In the future, this will collect cloud information and make a smooth functioning of Industry 4.0.


