Co3O4 Nanoparticles as a Noninvasive Electrochemical Sensor for Glucose Detection in Saliva
Abstract
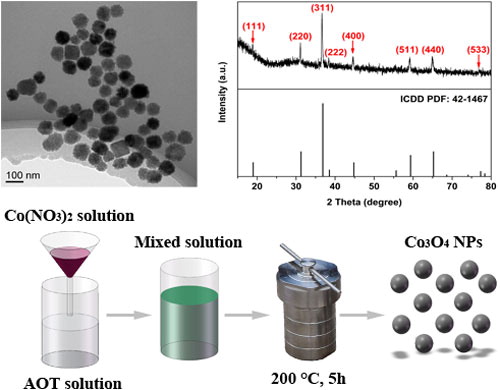
A new noninvasive glucose sensor is developed based on Co3O4 particles (Co3O4 NPs), which are synthesized by a single-step hydrothermal method with uniform structure and size. The electrochemical measurements reveal that the device exhibits outstanding performance for glucose detection, achieving a maximal sensitivity of 2495.79μA mM−1 cm−2 with a high R2 of 0.99575, a ultra-low detection limit of 9.3nM with a signal-to-noise of 3 and linear range up to 3mM. The noninvasive glucose sensor can respond swiftly and selectively due to the high electrocatalytic activity of Co3O4 NPs. The sensor also shows its high sensitivity and selectivity in detecting glucose levels in human blood serum and saliva sample, confirming the application potential of Co3O4 NPs in noninvasive detection of glucose.