Corneal damage effects induced by infrared optical parametric oscillator radiation at 3743 nm
Abstract
The main aim of this paper is to investigate the corneal damage effects induced by mid-infrared optical parametric oscillator (OPO) radiation. Experiments were performed to determine the corneal damage thresholds of New Zealand white rabbit at the wavelength of 3743nm for exposure durations of 0.1s, 1.0s and 10.0s. Through slit-lamp biomicroscope and histopathology, corneal injury characteristics were revealed. The damage thresholds were 3.73J/cm2, 7.91J/cm2 and 31.1J/cm2, respectively, for exposure durations of 0.1s, 1.0s and 10.0s. The damage data was correlated by an empirical equation: Radiant exposure at the threshold=9.72×exposurethreshold=9.72×exposure duration,0.460.46 where the units of radiant exposure and exposure duration were J/cm2 and second. At near-threshold level, corneal injuries at 1 h post-exposure mainly involved the epithelium, and the epithelium damages repaired at 24-h post-exposure. There are sufficient safety margins between the damage thresholds and the maximum permitted exposures from current international laser safety standard IEC 60825-1.
1. Introduction
Infrared lasers in the wavelength range of 3–5μμm have been increasingly applied in diverse fields such as environmental monitoring,1 precise spectrum analysis2 and infrared countermeasures.3 Optical parametric oscillator (OPO) technology is receiving much attention in recent years because it is a practical approach to generate lasers operating in this wavelength range, comparing to chemical deuterium fluoride lasers developed in 1970s.4,5,6,7,8,9 With the breakthrough on nonlinear crystals and fiber lasers, technology in fiber laser pumped OPO developed rapidly and the output power increased continually.10,11,12,13,14 In international public reports, the maximum power of continual-wave infrared OPO laser has been increased above 30W, with the wavelength tuning range of 3.2–3.9μμm.15
Because of the importance of vision and increasing applications of OPO sources, attention has to be paid to the potential ocular injuries induced by OPO sources. In the wavelength range above 1.4μμm, ocular damages mainly occur at the cornea because radiation is significantly absorbed in the cornea and aqueous humor.16 Vision can be decreased significantly and permanently due to severe corneal injuries.17 For the protection of cornea, a large amount of studies have been conducted to determine the corneal injury thresholds induced by CO2 laser at the wavelength of 10.6μμm,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31 thulium laser at 2.0μμm32,33,34 and erbium laser at 1.54μμm.35,36,37,38,39,40,41 Corneal damage data from these studies promoted the developments of laser safety guidelines and standards.16,42,43 However, research on the damage effects induced by infrared OPO radiation in the wavelength range of 3–5μμm is lacking, thus it is necessary to perform experimental research on the corneal injury effects induced by mid-infrared OPO sources and examine whether the maximum permissible exposures (MPEs) specified in the current international safety standards are appropriate for evaluating the hazard of mid-infrared OPO sources. With above considerations, we performed experiments to determine the rabbit in-vivo corneal damage thresholds induced by an OPO source operating at 3743nm for exposure durations of 0.1s, 1.0s and 10.0s, revealed the corneal injury characteristics through slit-lamp microscope and histopathology, and compared the determined damage values with corresponding MPEs in the laser safety standards.42,43 The obtained results may provide references for the refinement of laser safety standard and the clinical treatments of accidental laser-induced corneal damages.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental set-up for corneal exposures by OPO source
The experimental set-up is shown in Fig. 1. The fiber laser pumped MgO: PPLN OPO was provided by National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China. The output of the OPO source included three kinds of laser radiation, with the wavelengths of 1070nm (pump laser), 1498nm (signal laser) and 3743nm (idler laser). Two mirrors, M1 and M2, were employed to separate the idler laser with the pump and signal lasers. The mirrors had a high reflectivity (R>99%R>99%) in the wavelength ranges of 1.0–1.1μμm and 1.4–1.7μμm, and a high transmittance (T>95%T>95%) in the wavelength range of 2.5–4.1μμm with the incidence angle of 45∘45∘. A laser spectrum analyzer (721B, Bristol Instruments Inc., NY, America) was used to measure the spectral component of the radiation after the mirror M2. As shown in Fig. 2, only a single line existed with the central wavelength of 3743nm and FWHM of 8 nm. The maximum power of the idler laser was about 8.3W, and the relative power fluctuation was within ±5.0%±5.0%. A fixed portion of the idler laser was reflected to the laser power meter 1# (3A, Ophir, Israel) by a GaF2 beam splitter with the wedge angle of 8∘8∘. Thus, the stability of the laser power during laser exposures could be monitored. Another laser power meter 2# (30A, Ophir, Jerusalem, Israel) was positioned to measure the power of the laser incident on the rabbit cornea. Through the adjustments of the driving current of the OPO source and adding attenuators including GaF2 plates and K9 plates, the laser power incident on the animal cornea could be changed freely. The exposure duration was controlled by an electronically-controlled mechanical shutter. The selected exposure durations were 0.1s, 1.0s and 10.0s. Two low-power 655-nm laser pointers, crossed at the center of the laser spot, facilitated the targeting of the invisible infrared laser radiation. A GaF2 plane-convex lens, with focal length of 500mm, was employed to change the spot size on the animal cornea. The distance between the lens and the rabbit cornea surface was kept constant as 28.3cm. At the corneal surface, the laser irradiance was nearly Gaussian-distributed. Using the knife-edge method,44 the 1/e beam diameters in the horizontal and vertical directions were determined as about 1.61mm and 1.50mm, respectively.
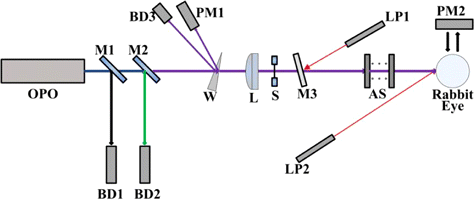
Fig. 1. Schematic drawing of the exposure setup for the determination of rabbit corneal damage thresholds induced by an infrared OPO (OPO: Fiber laser pumped MgO: PPLN OPO. M1: Mirror having a high reflectivity (R>9R>99%) in the wavelength ranges of 1.0–1.1μμm and 1.4–1.7μμm and simultaneously having a high transmittance (T>95%T>95%) in the wavelength range of 2.5–4.1μμm. M2: Mirror having same coatings with the mirror M1. BD1: Beam dump for collecting the pump and signal lasers. BD2: Beam dump for collecting the residual pump and signal lasers. W: GaF2 beam splitter with the wedge angle of 8∘8∘. BD3: Beam dump for collecting the idler laser radiation reflected from the first surface of the wedge beam splitter. PM1: Laser power meter 1#. L: GaF2 plane-convex lens with the focal length of 500mm. S: Electronically-controlled mechanical shutter. M3: GaF2 plate. LP1: Low-power 655nm laser pointer 1#. AS: Attenuators including GaF2 plates and K9 plates. LP2: Low-power 655 nm laser pointer 2#. PM2: Laser power meter 2#).
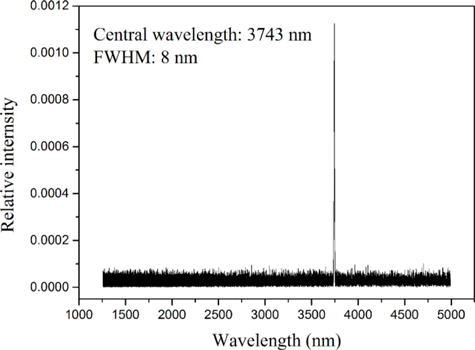
Fig. 2. The spectrum after M2, showing that the radiation incident on the rabbit cornea contained a single line with the central wavelength of 3743nm.
2.2. Animal subjects
New Zealand white rabbits were selected. The total number was 13 with weight of 2.5–3.2kg. The protocols and handling of the animals had been approved by the ethics review board of Academy of Military Medical Science, Beijing, China. All animals were procured and maintained in the Center for Laboratory Animal Medicine and Care, Academy of Military Medical Sciences, Beijing, China and used in accordance with the institutional guidelines of the Animal Care and Use Committee; and the ARVO Resolution on the Use of Animals in Research. A slit-lamp microscope (Topcon, Tokyo, Japan) and a fundus camera (Topcon, Tokyo, Japan) were employed to examine the animal eyes. Only the subjects with clear refractive media and healthy fundus were included. Before laser exposures, subjects were anesthetized with an intramuscular injection of a mixture of ketamine hydrochloride (20mg/kg) and xylazine (5mg/kg). Full pupil dilation was performed with two drops of proparacaine hydrochloride 0.5%, phenylephrine hydrochloride 2.5% and tropicamide 1% at a 5-min interval, which facilitated the following observations of corneal injuries. The anesthetized subjects were positioned with the aid of the two laser pointers. Corneal drying was prevented by periodic applications of physiological saline solution at room temperature and by manual blinking of the lids. Irrigation was stopped about 30s prior to laser exposures and the excess fluid was blotted at the limbus.
2.3. Damage determination and experimental procedures
The criterion for the determination of minimal epithelial damage is the presence of a superficial, barely visible, gray-white spot that develops within 1h after exposure.39 Corneas were assessed with a slit-lamp microscopy (Topcon, Tokyo, Japan). We refitted the slit-lamp microscopy by adding an eyepiece adaptor and a Huawei P20 cell phone, thus the corneal damage images could be captured. Two illumination methods, including broad-beam diffuse illumination and slit-beam illumination, were employed to observe the corneal lesions.
In the experiments, we found the damage threshold was well defined. The overlap between exposures that produced minimal lesions and those that did not was rare. Thus, the probit analysis was not employed to determine the damage threshold, as the statistical procedures would require using more animals than necessary.39 Specifically, we irradiated the rabbit cornea with step-changed incident power levels. The bracket between the power level (PHPH) producing a minimal lesion and that (PLPL) producing no damage was narrowed until only about a 10% difference existed between the PHPH and PLPL. The damage threshold PthPth then was 1determined as (PH+PL)∕2(PH+PL)∕2. As an example, Table 1 shows the damage results for the exposure duration of 1.0s. The peak radiant exposure HH shown in the table was defined by
| Laser power incident at the corneal surface PP (W) | Peak radiant exposure HH (J/cm2) | H∕Hthreshold | Involved eye number | Number of damage lesions/Number of exposures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.296 | 15.6 | 1.97 | 2 | 2/2 |
| 0.221 | 11.7 | 1.47 | 1 | 3/3 |
| 0.193 | 10.2 | 1.29 | 1 | 6/6 |
| 0.172 | 9.1 | 1.15 | 1 | 6/6 |
| 0.158 | 8.3 | 1.05 | 1 | 5/6 |
| 0.141 | 7.4 | 0.94 | 1 | 0/6 |
| 0.124 | 6.5 | 0.83 | 1 | 0/6 |
Additionally, we performed histopathologic studies. Some rabbits were euthanized at 6h and 24h post-exposure. After the euthanasia, eyeballs were taken and fixed in Davidson solution for 30min and then corneas were cut off and fixed in Davidson solution for 2.5h. The next steps were to dehydrate the corneas with ethanol, embedded with paraffin, serially sectioned and the sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). The histological images were captured by a microscope (BX43F, Olympus, Japan).
3. Results
Table 2 shows the determined damage thresholds for the exposure durations of 0.1s, 1.0s and 10.0s. The MPEs in the IEC-60825 standard43 and safety factors of HthresholdHthreshold/MPE were also included.
| Exposure duration (s) | Damage threshold expressed in power incident on the cornea PthresholdPthreshold (W) | Damage threshold expressed in peak radiant exposure HthresholdHthreshold (J/cm2) | MPE (J/cm2) | Safety factor of HthresholdHthreshold/MPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.708 | 3.73 | 0.31 | 12.0 |
| 1.0 | 0.150 | 7.91 | 0.56 | 14.1 |
| 10.0 | 0.059 | 31.1 | 1.00 | 31.1 |
Figure 3 shows the rabbit corneal lesions at 1-h post-exposure for the exposure duration of 1.0s and incident power of 0.158W (1.05 times the damage threshold). At the slightly-above threshold level, barely visible gray-white lesions could be observed for the exposure sites under slit-lamp microscopy with diffuse illumination (Fig. 3(a)). With slit-beam illumination, superficial reflective white straps could be seen, indicating that the threshold damage mainly involves the epithelium layer (Fig. 3(b)). The meaning of “white strap” is explained as follows. The normal cornea is transparent to incident light, but if damaged, the incident light would be significantly scattered by the damaged tissue which looks like “white strap” under slit-lamp microscopy. At 24-h post-exposure, these lesions could not be found, indicating that the damaged epithelium repaired. At 1.97 times of damage threshold, apparent and opaque lesion on corneal surface with circular symmetry could be found under broad-beam diffuse illumination. Surface distortion could also be found for the lesion and the lesion edge was distinct from surrounding normal tissue (Fig. 4(a)). With slit-beam illumination, highly reflective white strap with a thickness less than the cornea thickness was observed, showing that the damage involves the epithelium and part of the stroma (Fig. 4(b)). At 24-h post-exposure, the lesion became blurred and the edge was no longer distinct from surrounding tissue (Fig. 4(d)). Histological section at 6-h post-exposure showed that the epithelium layer disappeared and the number of cell nuclei in the partial stroma decreased obviously due to laser irradiation (Fig. 4(c)). At 24-h post-exposure, the epithelium repair could be found (Fig. 4(f)).
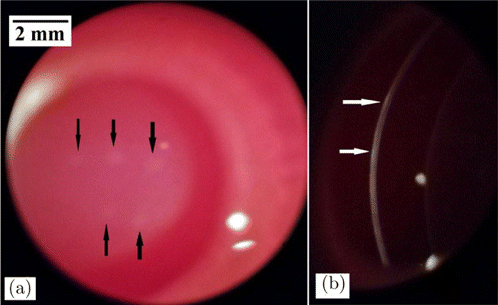
Fig. 3. Corneal damages with the exposure duration of 1.0s and the incident power of 0.158W (1.05 times the damage threshold). The arrows in the images indicated the lesions. (a) Lesions at 1-h post-exposure with broad-beam diffuse illumination and (b) Lesions at 1-h post-exposure with slit-beam illumination.
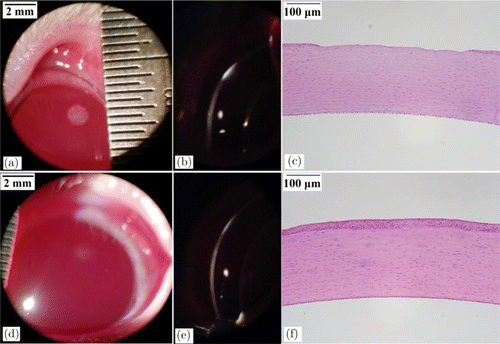
Fig. 4. Corneal damages with the exposure duration of 1.0s and the incident power of 0.296W (1.97 times the damage threshold). (a) Lesion at 1-h post-exposure with broad-beam diffuse illumination. (b) Lesion at 1-h post-exposure with slit-beam illumination. (c) Histological section at 6-h post-exposure. (d) Lesion at 24-h post-exposure with broad-beam diffuse illumination. (e) Lesion at 24-h post-exposure with slit-beam illumination and (f) Histological section at 24-h post-exposure.
4. Discussion
Previous corneal damage studies employed rabbit and rhesus monkey as the animal model. It is found that no significant difference for damage threshold values exists between the rabbit and the rhesus.45 Considering the current trends toward the reduction, refinement and replacement philosophy in animal research, use of nonhuman primates should be avoided and the rabbit model was selected to investigate the corneal damage effects induced by mid-infrared OPO radiation.41 For infrared laser radiation, the corneal injury is governed by thermal mechanism above about 50μμs.29,39 In the thermal-mechanism regime, the damage threshold variation with exposure duration could be correlated by a power function law :
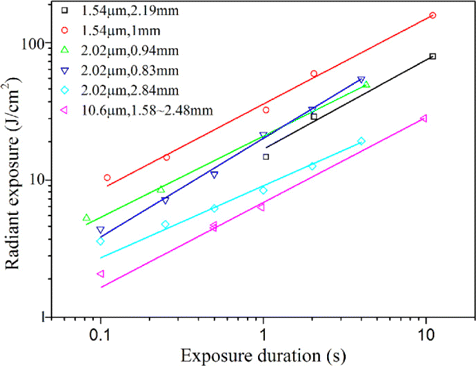
Fig. 5. Previous corneal damage thresholds.29,32,34,39 The parameters behind the symbols denoted the laser wavelength and the corneal 1/e spot diameter. The threshold data followed an empirical power-laser relationship Hthreshold=AtkHthreshold=Atk, where HthresholdHthreshold and tt was the radiant exposure at the threshold and the exposure duration; AA and kk was fitted constant values. Power-law fitting curves in the figure showed that the values of kk ranged from about 0.53–0.72.
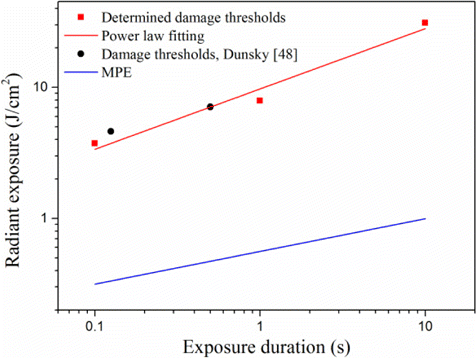
Fig. 6. Corneal damage thresholds at the wavelength of 3743nm and MPE curve for the wavelength range of 2600–106nm. The fitting curve followed the empirical power-law relationship Hthreshold=9.72t0.46Hthreshold=9.72t0.46, where HthresholdHthreshold and tt was the radiant exposure at the threshold and the exposure duration.
5. Conclusion
Corneal injuries induced by an OPO source at the wavelength of 3743nm were performed in the New Zealand white rabbit model. The corneal damage thresholds for exposure durations of 0.1s, 1.0s and 10.0s were 3.73J/cm2, 7.91J/cm2 and 31.1J/cm2, respectively. The damage values followed an empirical power-law equation. At threshold level, corneal damages at 1-h post-exposure mainly involved the epithelium. At 24-h post-exposure, the epithelium damages repaired. There were enough safety margins between the damage thresholds and corresponding MPEs, indicating that the MPEs in the laser safety standard are sufficient to protect the cornea at the wavelength of 3743nm.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (61575221).