Adsorption, Kinetic and Regeneration Studies of n-Hexane on MIL-101(Cr)/AC
Abstract
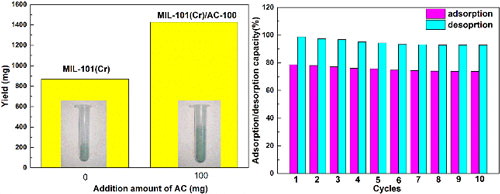
MIL-101(Cr)/AC was synthesized by in situ incorporation of activated carbon powder via hydrothermal method. The water stability, n-hexane adsorption and regeneration of the MIL-101(Cr)/AC were experimentally measured. The results showed that the MIL-101(Cr)/AC exhibited the larger surface area (3319.3m2/g) than that of MIL-101(Cr) and AC, respectively. The addition of activated carbon was beneficial to improve the yield of MIL-101(Cr)/AC. The pore structure parameter and XRD of the MIL-101(Cr)/AC changed little after in water for 24h. Furthermore, the adsorption capacity of MIL-101(Cr)/AC for n-hexane was 786mg/g, which increased to 23.0% and 27.7% compared with MIL-101(Cr) and AC, respectively. Kinetic fitting of data indicated that the pseudo-first order model can more accurately describe the adsorption process of n-hexane on MIL-101(Cr)/AC and the intraparticle diffusion was not the sole rate-controlling step. Besides, the regeneration efficiency of MIL-101(Cr)/AC was over 92% after 10 consecutive n-hexane adsorption/desorption cycles.